Projector

Film projector
This type of projector uses film reels to project moving images onto a screen. Film projectors are typically used in traditional movie theaters and are known for their high image quality.

Digital projector
This type of projector uses a digital video source, such as a computer or Blu-ray player, to project images onto a screen. Digital projectors are becoming increasingly popular in theaters due to their ease of use and flexibility.

DLP (Digital Light Processing) projector
This type of projector uses a DLP chip to process and project digital images onto a screen. DLP projectors are known for their high contrast and color accuracy.

LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) Projector
This type of projector uses a liquid crystal display to project images onto a screen. LCD projectors are known for their brightness and ease of use, but they can have a lower contrast than DLP projectors

LCoS (Liquid Crystal on Silicon) Projector
This type of projector uses a liquid crystal on a silicon panel to project images onto a screen. LCoS projectors are known for their high resolution and color accuracy.

LED/Laser projector
this type of projector uses a light-emitting diode (LED) or laser as light source, and projects the image, it's energy-efficient, long-lasting and has a wide color gamut.

Hybrid projector
a projector that uses two or more technologies for the projection.
Screen

Fixed Screens
These screens are mounted in a permanent frame and are typically used in home theaters and small conference rooms. Fixed frame screens are available in a variety of sizes and aspect ratios, and can be made from a variety of materials such as vinyl, fabric, or tensioned materials.

Manual Pull Down Screens
These screens are mounted on a roll and can be manually pulled down when needed. They are typically used in small conference rooms and classrooms, and can be made from a variety of materials such as vinyl or fabric.
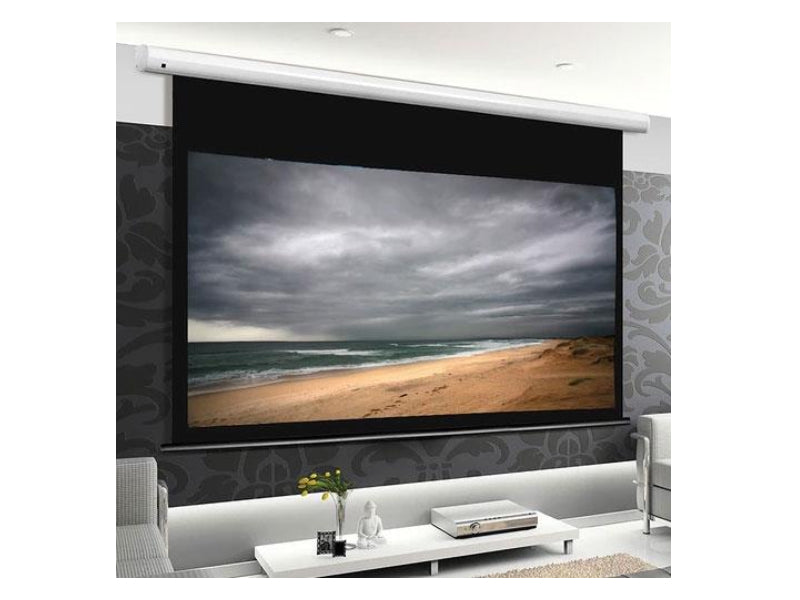

Motorized Screens
These screens can be raised and lowered using a motor with a remote control, and are typically used in large conference rooms and home theaters. Motorized screens are available in a variety of sizes and aspect ratios, and can be made from a variety of materials such as vinyl or fabric.
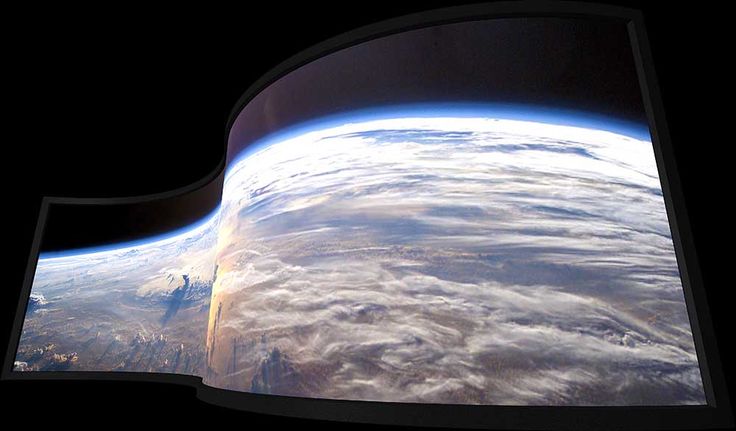

Curved Screens
These types of screens have a curved shape, this is to enhance the image, and make the viewer experience more immersive. The curvature of the screen creates a more uniform image and a wider field of view, making the image appear more natural and lifelike. One of the main advantages of curved screens is that they reduce the distortion that can occur at the edges of a flat screen. The edges of the screen are pulled inwards, which means that the edges of the image appear more natural, and the center of the screen is not distorted.
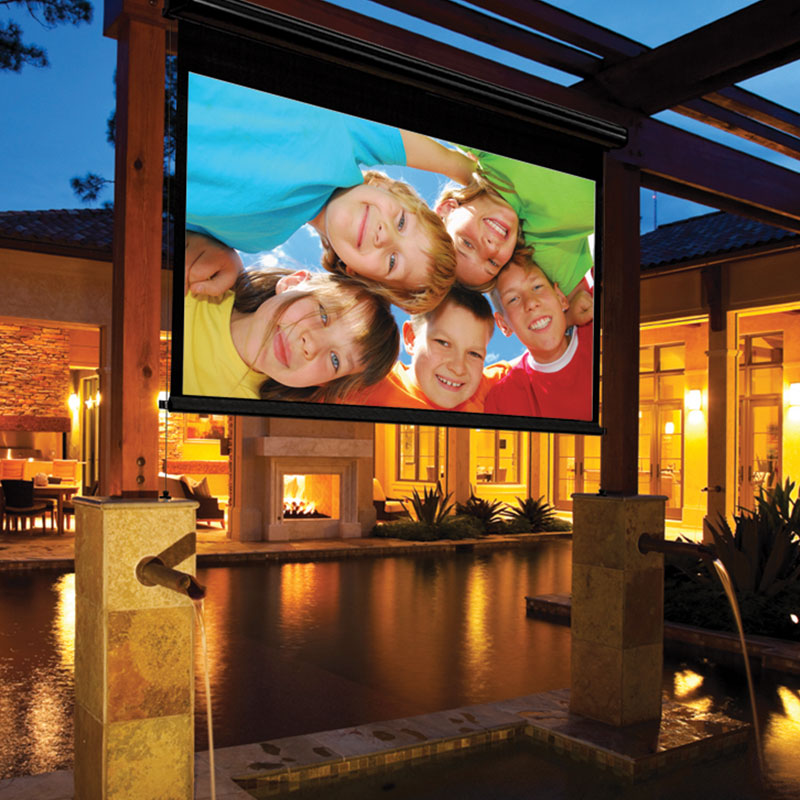

Outdoor Screens
These screens are designed to be used outdoors and are made from materials that can withstand the elements. They typically have a higher gain and a wider viewing angle to accommodate for ambient lighting.
Accoustic Screens
Acoustic screens are projector screens specifically designed to improve the audio experience in a room. They are often used in spaces such as home theaters, conference rooms, and performance venues. These screens typically feature a perforated surface that allows sound to pass through, but with a dampening effect. They may also be designed to help control the direction of sound, directing it towards the audience rather than reflecting it back towards the projector.
Sound
Speakers: Important Factors to Consider

Size and design: Consider the design and finish of the speakers to ensure they complement your existing decor and style. Whether you prefer sleek, modern lines or a more classic look, selecting speakers that blend seamlessly with your room’s aesthetic will enhance both the visual appeal and your overall listening experience.

Number of speakers: A typical home theater setup includes a center channel speaker, left and right front speakers, left and right surround speakers, left and right
surround back speakers, and possibly Atmos speakers.

Power and sensitivity: Make sure the speakers can handle the power output of your AV receiver.

Placement and mounting of the speakers: Are you mounting them onto a wall or floor standing? Do you need in-ceiling speakers for the surround speakers?
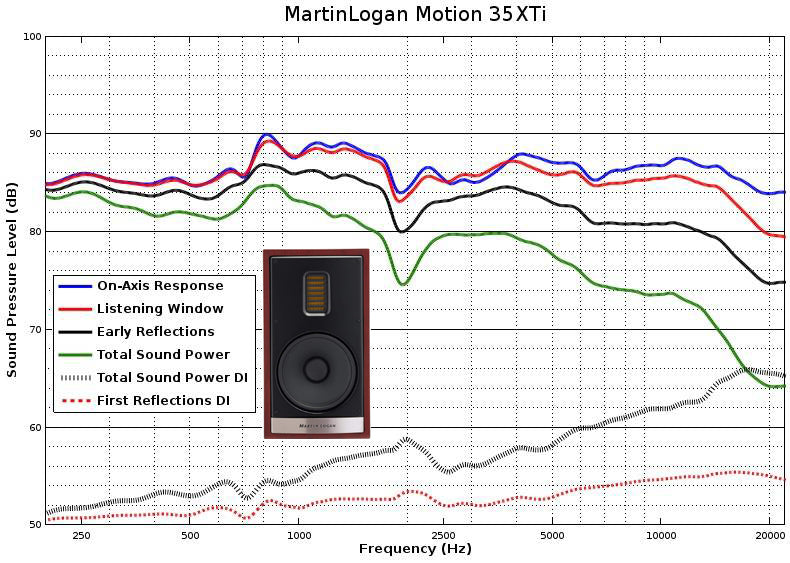
Frequency response: Look for speakers with a wide frequency response for clear and detailed sound.
AV Receiver: Important Factors to Consider

Number of channels: Look for a receiver with enough channels to support your speaker setup. A 5.1-channel receiver supports a 5.1-channel speaker setup (left, center, right, left surround, right surround, and subwoofer), while a 7.1-channel receiver supports a 7.1-channel speaker setup (left, center, right, left surround, right surround, left back, right back, and subwoofer)
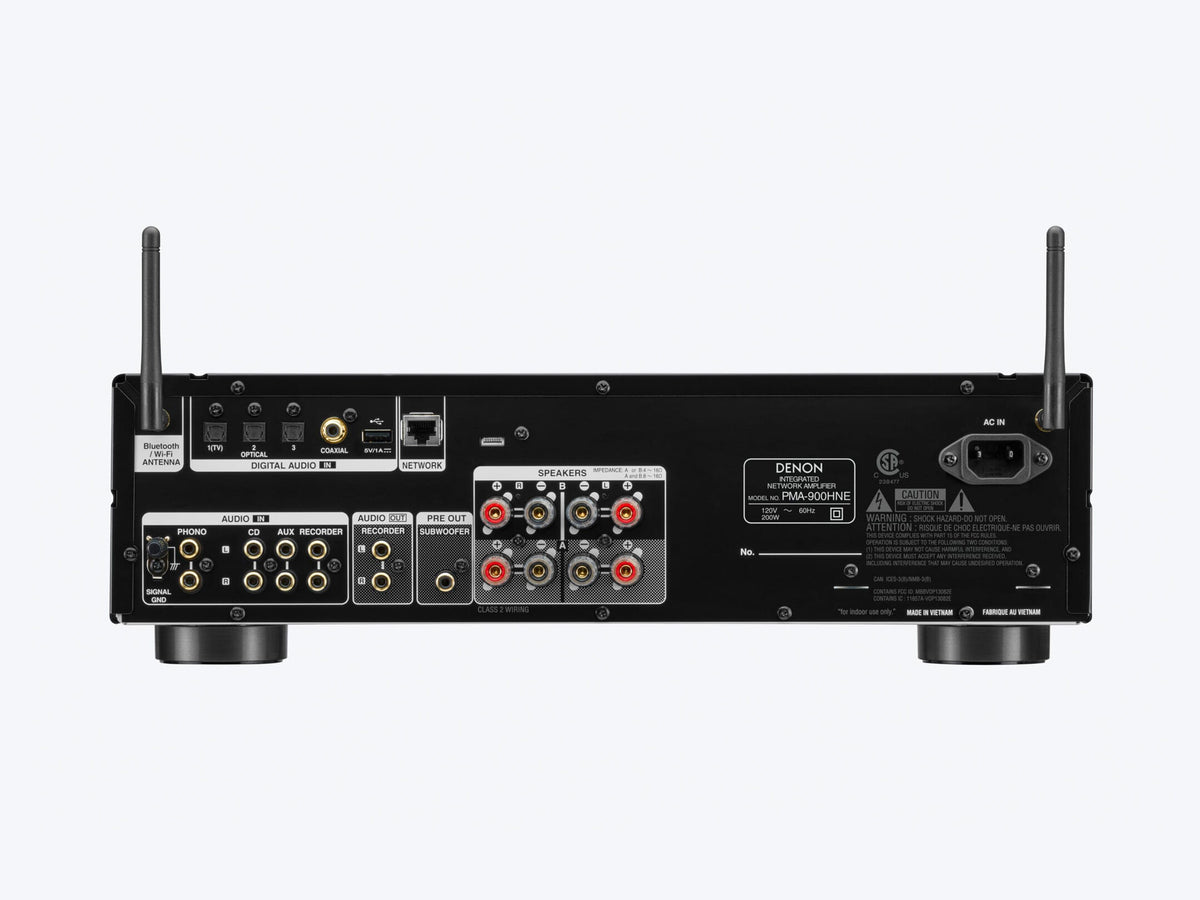

Power output: Make sure the receiver can handle the power output of your
speakers and has enough power to drive them to your desired volume
level.
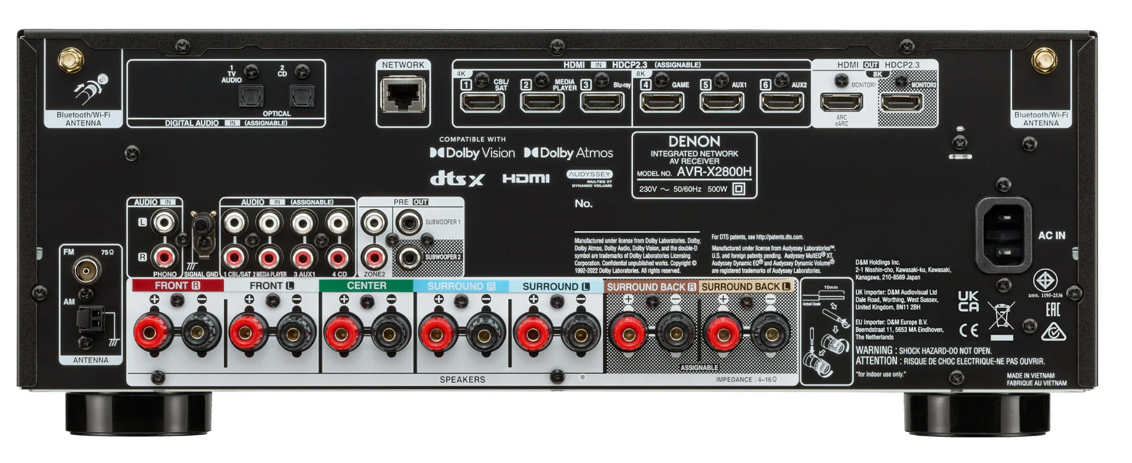

Compatibility and Connectivity: It’s essential to verify that it is compatible with all the devices you plan to connect, such as Blu-ray players, streaming devices, and gaming consoles. Equally important is checking that the receiver offers the necessary connectivity options, including HDMI, USB, and Ethernet ports, to support your current setup and future upgrades.
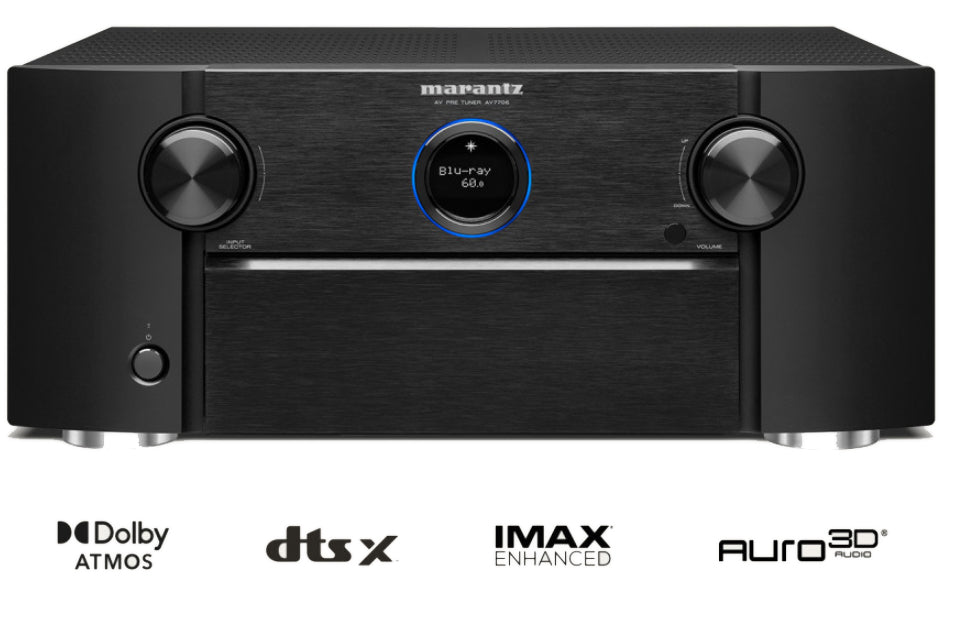

Audio and video processing: Look for a receiver with advanced audio and
video processing features, such as Dolby Atmos, DTS:X, and 4K HDR
pass-through, for an enhanced viewing and listening experience

Brand, Price, Warranty & Smart Features: it’s important to research the reputation of different brands and read customer reviews to get a clear idea of each model’s performance and reliability. Pay close attention to the price and warranty offered, ensuring you get good value and peace of mind with your purchase. Additionally, consider smart functionality features such as compatibility with smartphone apps or home automation systems, which can add convenience and flexibility to your setup.
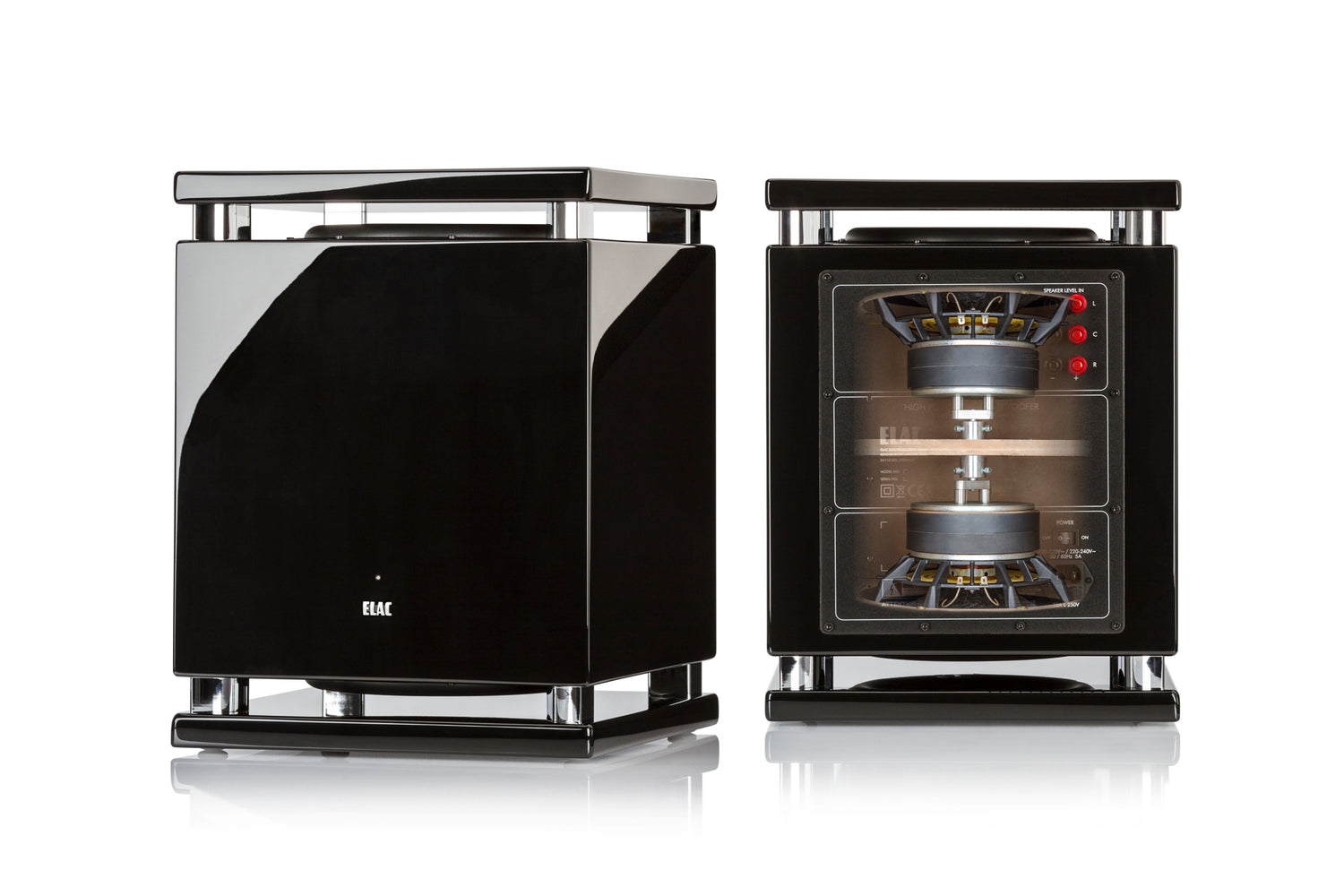
Subwoofer: Important Factors to Consider

Size, Design, and Placement: Ensure it not only fits comfortably in your room and complements your decor but also has an ideal placement. The location of the subwoofer can significantly affect sound quality and performance, so plan ahead to find a spot that delivers the best bass response without disrupting your space. Balancing size, design, and placement will help you achieve both great sound and a seamless look in your room.

Type of subwoofer: There are two main types of subwoofers: sealed and
ported. Sealed subwoofers are more precise and accurate, while ported
subwoofers are more efficient and produce more bass.

Power and frequency response: Look for a subwoofer with enough power to handle the demands of your room and speakers, and a frequency response that extends down to at least 20Hz, the lower limit of human hearing.

Reputation, Price, and Connectivity: Research brand reputation and read customer reviews to ensure reliable performance. Consider the price and warranty to get good value and protection. Also, check that the subwoofer’s connection options match your AV receiver or amplifier for easy setup and optimal sound.
It’s always a good idea to listen to speakers, amps, and subwoofers in-store before buying. Hearing them firsthand lets you judge sound quality, bass response, and how well they fit your preferences—something specs and reviews can’t fully capture. Plus, you can compare different models side by side and get expert advice to find the best match for your room and budget. This hands-on experience helps ensure you make a confident, satisfying purchase.









